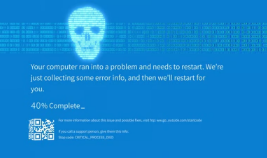
The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), also known as a stop error, is one of the most dreaded experiences for Windows users. When your computer suddenly crashes, displays a blue screen with an error message, and halts operation, it can be confusing and frustrating. Understanding what causes the BSOD and how to troubleshoot it can help you resolve issues and get your PC back on track.
What Is the Blue Screen of Death?
The BSOD appears when Windows encounters a critical error from which it cannot recover safely. To prevent potential damage, the system halts and displays a blue screen with technical information about the error. This screen is a safeguard designed to protect data and hardware.
Common Causes of BSOD
Several factors can lead to a BSOD, including:
- Hardware Problems: Faulty RAM, hard drives, overheating components, or failing power supplies.
- Driver Issues: Incompatible, outdated, or corrupted device drivers can cause system instability.
- Software Conflicts: Recently installed software or Windows updates may conflict with existing programs.
- Malware or Viruses: Malicious software can corrupt system files or interfere with normal operations.
- Overclocking: Running hardware components beyond their specifications may cause instability.
- System File Corruption: Corrupt or missing Windows system files can trigger errors.
Recognizing a BSOD
A typical BSOD will display:
- An error message with a specific error code (e.g.,
0x0000007E) - A brief description of the problem
- Sometimes, a URL or additional help information
- The system may automatically restart after the error
How to Troubleshoot and Fix BSODs
- Note the Error Code: Record the specific error code and message for reference.
- Reboot in Safe Mode: Boot your PC into Safe Mode to troubleshoot with minimal drivers and software.
- Update Drivers: Ensure all device drivers are current and compatible.
- Uninstall Recent Software: Remove any recently added programs that might be causing conflicts.
- Run Hardware Diagnostics: Test RAM, hard drives, and other hardware components for faults.
- Check for Windows Updates: Install any pending updates to fix known issues.
- Scan for Malware: Use antivirus tools to eliminate malicious infections.
- Use System Restore: Roll back to a previous state where your system was stable.
- Check for Overheating: Ensure your PC’s cooling system is functioning properly.
- Consult Logs: Use Event Viewer or Reliability Monitor to find detailed error information.
When to Seek Professional Help
If troubleshooting doesn’t resolve the problem, or if you experience persistent BSODs, it’s advisable to consult a professional technician. Continual crashes might indicate deeper hardware failures or complex software issues requiring expert diagnosis.